Meritshot Tutorials
- Home
- »
- Introduction to Ethical Hacking
Cyber Security Tutorial
-
What is cybersecurity?What is cybersecurity?
-
Introduction to LinuxIntroduction to Linux
-
Text Processing using GREP, SED, and AWKText Processing using GREP, SED, and AWK
-
Introduction to Ethical HackingIntroduction to Ethical Hacking
-
Footprinting and ReconnaissanceFootprinting and Reconnaissance
-
Scanning NetworksScanning Networks
-
Enumeration in Cyber SecurityEnumeration in Cyber Security
-
Vulnerability AnalysisVulnerability Analysis
-
System HackingSystem Hacking
-
Malware ThreatsMalware Threats
-
SniffingSniffing
-
Social EngineeringSocial Engineering
-
Denial-of-ServiceDenial-of-Service
-
Evading IDS, Firewalls, and HoneypotsEvading IDS, Firewalls, and Honeypots
-
Hacking Web ServersHacking Web Servers
-
Hacking Web ApplicationsHacking Web Applications
-
SQL InjectionSQL Injection
-
Hacking Wireless NetworksHacking Wireless Networks
-
Hacking Web ApplicationsHacking Web Applications
-
Hacking Mobile PlatformsHacking Mobile Platforms
-
IoT HackingIoT Hacking
-
Cloud ComputingCloud Computing
-
CryptographyCryptography
Introduction to Ethical Hacking
In today’s digital age, the importance of protecting computer systems and networks from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats cannot be overstated. Cybersecurity is a critical component of modern technology infrastructure, and ethical hacking plays a pivotal role in safeguarding these systems. Ethical hacking involves authorized professionals proactively identifying security vulnerabilities and addressing them before malicious actors can exploit them.
Unlike malicious hacking—where attackers exploit vulnerabilities for personal gain or destructive purposes—ethical hacking is a structured and authorized effort aimed at
strengthening system security. Ethical hackers, often referred to as white-hat hackers, conduct controlled and systematic assessments of systems, applications, and networks to uncover weaknesses. By doing so, they help organizations fortify their defenses against potential breaches and ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of their data.
This proactive approach enables ethical hackers to simulate real-world attack scenarios under controlled conditions. Their efforts help organizations stay one step ahead of cybercriminals by identifying and resolving vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Ethical hacking is not just a technical endeavor but also a strategic one, ensuring that organizations can meet compliance standards and maintain trust with their users.
In essence, ethical hacking is a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity, empowering organizations to stay resilient in the face of evolving threats.
What is Hacking?
Gaining access to a system that you are not supposed to have access is considered as hacking. For example: login into an email account that is not supposed to have access, gaining access to a remote computer that you are not supposed to have access, reading information that you are not supposed to able to read is considered as hacking. There are a large number of ways to hack a system.
In 1960, the first known event of hacking had taken place at MIT and at the same time, the term Hacker was organized.
What is Ethical hacking?
Ethical hacking is the practice of systematically probing and testing computer systems, networks, and applications to identify and resolve security vulnerabilities. Also
known as white-hat hacking or penetration testing, ethical hacking involves authorized professionals simulating the techniques and methodologies used by malicious hackers to strengthen an organization’s cybersecurity defenses.
The primary objective of ethical hacking is to proactively uncover weaknesses that could be exploited by cybercriminals. By addressing these vulnerabilities, organizations can protect sensitive information, ensure compliance with security standards, and maintain a robust security posture. Ethical hackers play a vital role in safeguarding digital assets and ensuring the integrity of systems and networks.
Unlike malicious hacking, ethical hacking is permission-based and fully authorized. This distinction is critical, as ethical hackers operate under clear legal boundaries and with the consent of the organization. Their work includes simulating real-world attack scenarios to identify potential threats, testing system defenses, and offering recommendations for improvements.
Key Aspects of Ethical Hacking:
- Permission-Based Testing: Ethical hackers operate with explicit authorization to perform security assessments, differentiating their work from illegal
- Objective-Driven: The goal is to find vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. This includes identifying flaws in systems, applications, and
- Methodology: Ethical hackers use the same tools, techniques, and methods as cybercriminals, including vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and security
- Reporting: Ethical hackers provide detailed reports outlining their findings, including identified vulnerabilities and actionable recommendations for
By adopting a proactive approach, ethical hacking empowers organizations to anticipate and mitigate potential threats, safeguard their digital infrastructure, and stay ahead in the constantly evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Importance of Ethical Hacking
Ethical hacking plays a crucial role in modern cybersecurity by proactively identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before malicious actors exploit them. By simulating the techniques and strategies of cybercriminals, ethical hackers help organizations safeguard their systems and data. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Security: Ethical hackers uncover and resolve security flaws, preventing data breaches and
- Regulatory Compliance: Organizations can meet industry standards and regulatory requirements for
- Risk Management: Ethical hacking helps assess and mitigate potential threats to organizational
- Incident Response: Strengthens an organization’s ability to respond to and recover from security incidents
In an era of escalating cybercrime, driven by threats like ransomware, malware, and viruses, ethical hacking is indispensable. With cybercriminals increasingly targeting
critical systems—sometimes backed by terrorist organization l security or extort large sums—organizations must continuously update their defense strategies.
By leveraging ethical hacking services, businesses, government agencies, and defense sectors can proactively safeguard their networks, ensuring resilience against the rapidly evolving threat landscape.
Benefits of Ethical Hacking?
The primary benefit of ethical hacking is to prevent data from being stolen and misused by malicious attackers, as well as:
- Discovering vulnerabilities from an attacker’s POV so that weak points can be
- Implementing a secure network that prevents security
- Defending national security by protecting data from
- Gaining the trust of customers and investors by ensuring the security of their products and
- Helping protect networks with real-world
Guide to Ethical Hacking

Types of Hacking
We can define hacking into different categories, based on what is being hacked. These are as follows:
- Network Hacking
- Website Hacking
- Computer Hacking
- Password Hacking
- Email Hacking
- Network Hacking: Network hacking means gathering information about a network with the intent to harm the network system and hamper its operations using the various tools like Telnet, NS lookup, Ping, Tracert, etc.
- Website hacking: Website hacking means taking unauthorized access over a web server, database and make a change in the
- Computer hacking: Computer hacking means unauthorized access to the Computer and steals the information from PC like Computer ID and password by applying hacking methods.
- Password hacking: Password hacking is the process of recovering secret passwords from data that has been already stored in the computer
- Email hacking: Email hacking means unauthorized access on an Email account and using it without the owner’s
Types of Ethical Hacking
It is no big secret that any system, process, website, device, etc., can be hacked. In order to understand how the hack might happen and what the damage could be, ethical hackers must know how to think like malicious hackers and know the tools and techniques they are likely to use.
Hacking the network: involves testing the infrastructure of the network in order to find flaws in the protocols, configurations, and devices of the network
Hacking Web Applications: Centers around distinguishing shortcomings in web applications, for example, SQL injection or cross-website prearranging (XSS) weaknesses
Hacking the system: Targets working frameworks and programming to find security defects that could be taken advantage of.
Social Designing: attempts to manipulate individuals into revealing confidential information or performing actions that could compromise security, putting the human element to the test.
Hacking into wireless networks: involves identifying potential dangers in wireless communications and evaluating the security of wireless networks.
Types of Ethical Hackers
A Hacker is a person who is intensely interested in the mysterious workings of any computer operating system. Hackers are most often programmers. They gather advanced knowledge of operating systems and programming languages and discover loopholes within systems and the reasons for such loopholes. In this article, we will learn about all types of hackers, the Difference between White, black and, grey hat hackers, ways to protect against them.
- White Hat Hackers (Cyber-Security Hacker)
- Black Hat Hackers (Cracker)
- Gray Hat Hackers (Both)
- Blue Hat hackers
- Green Hat Hackers
- Red Hat
- State/Nation Sponsored
- Malicious Insider or
- Malicious Insider or
- White Hat Hackers: Here, we look for bugs and ethically report them to the We are authorized as a user to test for bugs in a website or network and report it to them. White hat hackers generally get all the needed information about the application or network to test for, from the organization itself. They use their skills to test it before the website goes live or attacked by malicious hackers. To become a white hat hacker, you can earn a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, or cybersecurity. In addition, certifications such as Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) are highly recommended.
- Black Hat Hackers: Here, the organization doesn’t allow the user to test it. They unethically enter inside the website and steal data from the admin panel or manipulate the data. They only focus on themselves and the advantages they will get from the personal data for personal financial gain. They can cause major damage to the company by altering the functions which lead to the loss of the company at a much higher This can even lead you to extreme consequences.
- Grey Hat Hackers: They sometimes access to the data and violates the law. But never have the same intention as Black hat hackers, they often operate for the common good. The main difference is that they exploit vulnerability publicly whereas white hat hackers do it privately for the company.One criticism of Grey Hat hackers is that their actions can still cause harm. Even if they do not steal or damage data, their unauthorized access to computer systems can still disrupt operations and cause financial losses for companies. Additionally, there is always the risk that a Grey Hat hacker will accidentally cause damage while attempting to identify
- Blue Hat hackers: They are much like the script kiddies, are beginners in the field of hacking. If anyone makes angry a script kiddie and he/she may take revenge, then they are considered as the blue hat hackers. Blue Hat hackers payback to those who have challenged them or angry them. Like the Script Kiddies, Blue hat hackers also have no desire to learn.
- Green Hat hackers : They are also amateurs in the world of hacking but they are bit different from script kiddies. They care about hacking and strive to become full- blown hackers. They are inspired by the hackers and ask them few questions about. While hackers are answering their question they will listen to its
- Red Hat Hackers: They are also known as the eagle-eyed hackers. Like white hat hackers, red hat hackers also aims to halt the black hat hackers. There is a major difference in the way they operate. They become ruthless while dealing with malware actions of the black hat hackers. Red hat hacker will keep on attacking the hacker aggressively that the hacker may know it as well have to replace the whole
- Script Kiddies: They are the most dangerous people in terms of hackers. A Script kiddie is an unskilled person who uses scripts or downloads tools available for hacking provided by other hackers. They attempt to attack computer systems and networks and deface websites. Their main purpose is to impress their friends and Generally, Script Kiddies are juveniles who are unskilled about hacking.
- State/Nation Sponsored Hackers: State or Nation sponsored hackers are those who are appointed by the government to provide them cybersecurity and to gain confidential information from other countries to stay at the top or to avoid any kind of danger to the They are highly paid government workers.
- Hacktivist: These are also called the online versions of the activists. Hacktivist is a hacker or a group of anonymous hackers who gain unauthorized access to government’s computer files and networks for further social or political
- Malicious Insider or Whistleblower: A malicious insider or a whistleblower could be an employee of a company or a government agency with a grudge or a strategic employee who becomes aware of any illegal activities happening within the organization and can blackmail the organization for his/her personal
What’s the Difference Between White, Black, and Gray Hat Hackers?
White hat hackers are ethical hackers who help improve cybersecurity by identifying and fixing vulnerabilities in systems. They work with organizations to enhance security measures and protect sensitive data. Black hat hackers, on the other hand, engage in malicious activities for personal gain, exploiting system weaknesses to steal, alter, or destroy data. Gray hat hackers fall somewhere in between, as they may break laws or ethical guidelines but do not have malicious intent. Understanding the differences between white, black, and gray hat hackers is essential for grasping the diverse landscape of hacking and the various motivations behind these activities. By recognizing these distinctions, organizations can better address security challenges
and foster a safer digital environment

Phases of Ethical Hacking
Ethical hacking is a process of detecting vulnerabilities in an application, system, or organization’s infrastructure that an attacker can use to exploit an individual or organization. They use this process to prevent cyberattacks and security breaches by lawfully hacking into the systems and looking for weak points. An ethical hacker follows the steps and thought process of a malicious attacker to gain authorized access and test the organization’s strategies and network.
Ethical hacking typically involves the following key phases:
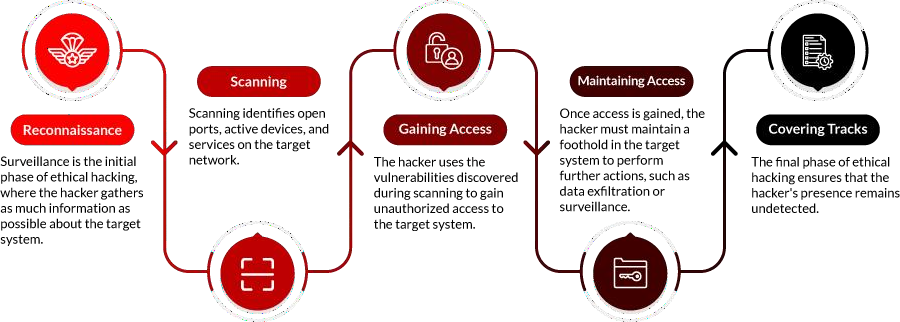
- Reconnaissance
Reconnaissance is the first step in ethical hacking. It’s often referred to as footprinting. Here, a hacker tries collecting various kinds of data, such as employee information, IP addresses, network topology, and domain names, using active and passive approaches. The purpose is to create a diagram of the target’s digital and physical assets.
Active Reconnaissance: This method involves direct interaction with the target system, which may warn the target about possible scans.
Passive Reconnaissance: This implies collecting data without direct contact with the target, making it untraceable.
Popular Tools Used are:
- Nmap
- Whois
- Maltego
Reconnaissance Techniques Commonly Used:
- Google Dorking: Utilizing sophisticated search operators to find sensitive information
- Whois Lookup: Collecting information on who owns the domain, IP addresses,
- Social Engineering: Mupulating people into revealing private information regarding targets; this can be done through phishing messages, for instance.
- DNS Enumeration: To create a topology of the target’s infrastructure by finding all DNS entries linked with the domain name concerned.
- Network Scanning: One can learn about active systems and running services using tools like
2. Scanning
At that point, the hacker goes to the scanning stage after having enough information. Scanning recognizes open ports, active devices, and services in the targeted network. It also helps to identify areas of vulnerability that can be targeted. Scanning is usually divided into three categories:
- Port Scanning: Finding open ports or services with Nmap or Angry IP
- Vulnerability Scanning: Detecting known weaknesses in systems and applications using Nessus.
- Network Mapping: Creating a blueprint of network topology with tools such as
Popular Tools Used:
- Nessus
- OpenVAS
- Angry IP Scanner
Commonly used techniques for Scanning
- Port Scanning: Using tools like Nmap or Angry IP Scanner to find open ports or
- Vulnerability Scanning: Using tools like Nessus to detect known weaknesses in systems and applications.
- Network Mapping: Generating a visual map that shows the network topology with applications like
- Banner Grabbing: This involves collecting software version information from open services to help determine any
- Ping Sweeps: This entails sending ICMP requests to identify active hosts on a particular network.
3. Gaining Access
During this crucial stage, the intruder utilizes the weaknesses identified during scanning for unauthorized entry into the target system. This may involve leveraging applications, operating systems, or network flaws. The objective is establishing access at different privilege levels, from user accounts to administrative control. Exploitation Methods comprise buffer overflows, SQL injection, and cross-site scripting (XSS).
Popular Tools Used:
- Metasploit
- SQLmap
- Hydra
Commonly used techniques for Gaining Access:
- Password Cracking: Using brute force and dictionary attacks or to crack passwords, rainbow tables are
- Exploration of Vulnerabilities: Unauthorized access can be obtained by exploiting known vulnerabilities such as SQL Injection or buffer
- Privilege Escalation: Higher-level privileges are acquired within a system through exploitation or
- Session Hijacking: Taking over a valid session between a user and a system gives entrance without
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks: By intercepting communication between two parties, sensitive data can be accessed, violating confidentiality principles.
4. Maintaining Access
Once inside, the intruder must maintain a presence on the target machine for further actions such as gathering or monitoring sensitive data. Therefore, backdoors, rootkits, or Trojan horses can be installed at this point to ensure continued access to the device even after it has been rebooted or patched. Persistence Techniques: Employing malicious programs, establishing concealed user accounts, or exploiting cron jobs.
Tools Used:
- Netcat
- Ngrok
- Empire
Standard Methods of Maintaining Access:
- Installing Backdoors: Creating permanent ways of accessing the system later, like backdoors or
- Creating Hidden User Accounts: Adding unauthorized users with administrative privileges that are hard to discover.
- Tunneling: Employing strategies such as SSH tunneling for secure communication with an infected machine.
- Keystroke Logging: Capturing user’s keystroke entries to acquire confidential details such as passwords or private
- Trojan Horses: Integrating applications that look real but permit unlawful
5. Clearing Track
The finale of ethical hacking revolves around ensuring the hacker remains under the radar. This implies wiping logs, concealing files, and manipulating timestamps to eliminate evidence or proof of any attack. The intention is to ensure that attackers can never be detected or traced via their attack methodology.
Tools Used:
- CCleaner
- Stealth Rootkit
- Timestomp
Standard Methods For Covering Tracks:
- Log Tampering: Deleting or modifying logs to erase evidence of hacking
- Steganography: Hiding malicious files or data within legitimate files to avoid
- File Timestamp Alteration: Changing the timestamps of modified files to mislead
- Clearing Command Histories: Deleting or altering shell command histories to prevent
- Encryption: Encrypting communication and files to obscure activities makes forensic analysis more
Core Concepts of System Hacking
System hacking involves a methodical approach to compromising and securing systems, typically for penetration testing or ethical hacking purposes. The core concepts include:
1. Footprinting
Footprinting means gathering information about a target system that can be used to execute a successful cyber attack. To get this information, a hacker might use various methods with variant tools. This information is the first road for the hacker to crack a system. There are two types of footprinting as following below.
Active Footprinting: Active footprinting means performing footprinting by getting in direct touch with the target machine.
Passive Footprinting: Passive footprinting means collecting information about a system located at a remote distance from the attacker.
Different kinds of information that can be gathered from Footprinting are as follows:
- The operating system of the target machine
- Firewall
- IP address
- Network map
- Security configurations of the target machine
- Email id, password
- Server configurations
- URLs
- VPN
2. Scanning
Scanning in ethical hacking is a network exploration technique used to identify the systems connected to an organization’s network. It provides information about the accessible systems, services, and resources on a target system. Some may refer to this type of scan as an active scan because it can potentially disrupt services on those hosts that are susceptible. Scanning is often used during vulnerability assessment when probing weaknesses in existing defenses.
There are two ways of scanning:
Active Scanning
Active scanning is a network scanning technique that actively interacts with a target system to gather detailed information, unlike passive scanning, which only observes available data. It involves sending requests or packets to identify vulnerabilities, open ports, and running services. Common methods include port scanning, vulnerability scanning, and penetration testing. While active scanning helps gather critical information for identifying weaknesses, it can also generate high traffic, strain systems, and trigger security measures like firewalls or intrusion detection systems (IDS), potentially alerting organizations to an attack.
Passive Scanning
Passive scanning is a network scanning technique that collects information about a target system or network without actively interacting with it. Unlike active scanning, which sends requests to the target and analyzes responses, passive scanning gathers information that is already available, such as network traffic and system logs. This method is used for network mapping, vulnerability assessment, and compliance testing, providing insights into infrastructure, servers, and services without triggering security defenses like firewalls or IDS. However, passive scanning is limited in its ability to probe for vulnerabilities compared to active scanning.
Types of scanning techniques include TCP connect scan, which determines open ports based on responses to TCP SYN packets, and TCP SYN port scan, which identifies open ports by sending TCP SYN packets and analyzing the responses.
Network scanning identifies devices and services on a network, while vulnerability scanning detects security weaknesses using automated tools.
3. Enumeration
Enumeration is the process of identifying all hosts on a network. This can be done in several ways, but active and passive scanning is the most common method. Active scanning involves sending out requests and analyzing the responses to determine which hosts are active on the network. Passive scanning involves listening to traffic and then analyzing it to identify hosts.
Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages. Active scanning is more likely to identify all hosts on a network, but it is also more likely to cause disruptions because it generates a lot of traffic. Passive scanning is less likely to identify all hosts, but it is also less likely to cause disruptions because it does not generate any traffic.
Types of Enumeration:
There are many different types of enumeration. The most appropriate type will depend on the situation and the required information:
- NetBIOS Enumeration: NetBIOS is a protocol that allows devices on a network to share resources and communicate with each other. NetBIOS enumeration is querying a device to identify what NetBIOS resources are available. This can be done using tools like nbtstat and net view.
- SNMP Enumeration: SNMP is a protocol that allows devices to be managed and monitored remotely. SNMP enumeration is querying a device to identify what SNMP resources are available. This can be done using tools like SNMP- check and snmpwalk.
- LDAP Enumeration: LDAP is a protocol that allows devices on a network to share information about users and resources. LDAP enumeration is querying a device to identify what LDAP resources are available. This can be done using tools like ldapsearch and ldapenum.
- NTP Enumeration: NTP is a protocol that allows devices on a network to synchronize their clocks with each other. NTP enumeration is querying a device to identify what NTP resources are available. This can be done using tools
like Nmap and PRTG Network Monitor .
4. Vulnerability Analysis
Vulnerability analysis is the systematic process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing security weaknesses in a system, network, or application. It helps organizations understand their exposure to potential threats and enables them to take proactive measures to mitigate risks.
Key Steps in Vulnerability Analysis:
- Discovery: Identify assets such as servers, applications, and network devices that need
- Scanning: Use tools to detect vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and outdated software versions.
- Evaluation: Analyze identified vulnerabilities to determine their potential impact and likelihood of
- Prioritization: Rank vulnerabilities based on severity, using metrics like CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System).
- Remediation: Develop and implement strategies to fix or mitigate vulnerabilities, such as applying patches or updating configurations.
Tools for Vulnerability Analysis:
- Nessus
- OpenVAS
- Qualys
- Metasploit
What is System Hacking in Ethical Hacking?
System hacking is the process of exploiting vulnerabilities in electronic systems for the purpose of gaining unauthorized access to those systems. Hackers use a variety of techniques and methods to access electronic systems, including phishing, social engineering, and password guessing.
Purpose of System Hacking:
Generally, the motive of the hackers behind System Hacking is gaining access to the personal data of an individual or sensitive information belonging to an organization in order to misuse the information and leak it which may cause a negative image of the organization in the minds of people, Privilege Escalation, Executing malicious applications to constantly monitor the system.
How this is carried out?
This type of hacking is generally done by a Hacker who has a lot of information regarding the System security, network, software, and how the system communicates with others in the network, often called Footprinting and Reconnaissance. Then these hackers try numerous ways to carry out the attack but the common ways are:
- By deploying Viruses, Worms, Malware, Trojans
- Using phishing techniques
- Social Engineering
- Identifying and exploiting Vulnerability
Steps:
- Reconnaissance: The first step in this type of Hacking is collecting information regarding the System’s infrastructure, working, system’s This step is very
important as after this step the Hacker knows what attack to perform and how to gain access without leaving a trace.
- Scanning: This step involves scanning the target System, which includes:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Checking vulnerabilities in the targeted system that can be exploited to gain access.
- Mapping of Network: Finding the working of the network, firewalls, routers, and systems connected to it.
- Port Scanning: Scanning the open ports, and services running over the System/Server.
- Gaining Access: This is the phase in which the hacker breaks into the system and gains unauthorized access to the System/Network and then elevates his privileges to that of Administrator or SuperUser so he can play with the System files that a normal/Guest user is unable to access.
- Maintaining the Access: After the Hacker enters the System he tries to maintain the connection with it in the background until he accomplishes the goal with which he entered
Prevention from Hacking:
- Using
- Installing Anti-Virus and Anti-Spyware
- Keeping the system up-to-date as security patches updates comes
- Be Aware of various phishing
Advantages of Hacking
There are various advantages of hacking:
- It is used to recover the lost of information, especially when you lost your
- It is used to perform penetration testing to increase the security of the computer and
- It is used to test how good security is on your
Disadvantages of Hacking
There are various disadvantages of hacking:
- It can harm the privacy of
- Hacking is
- Criminal can use hacking to their
- Hampering system
Summary
- Ethical hacking is a vital aspect of modern cybersecurity that involves using the same techniques as malicious hackers but for a positive purpose—identifying and fixing vulnerabilities in systems before they can be exploited. Ethical hackers actively test and simulate attacks on networks, applications, and other digital assets to uncover weaknesses. This proactive approach helps organizations identify flaws in their security measures, allowing them to address potential threats before they lead to data breaches, financial losses, or reputational
- Beyond just performing vulnerability assessments, ethical hackers conduct comprehensive security audits, analyze system configurations, and simulate real- world cyberattacks to test the effectiveness of existing defenses. They also provide organizations with practical recommendations to strengthen their security posture, such as patching vulnerabilities, improving encryption, and enhancing network segmentation.With the rapid advancement of cyber threats, including sophisticated malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks, ethical hacking has become increasingly crucial. Organizations must stay ahead of these evolving threats by investing in ethical hacking practices. Doing so not only improves security but also boosts stakeholder confidence, demonstrating a commitment to protecting sensitive information and maintaining trust in the digital age.




