INTRODUCTION:
Paytm, officially known as One97 Communications, has emerged as a leading force in India’s digital payment and financial technology sector. Founded in 2010, the company started as a mobile recharge platform and has since expanded into a comprehensive financial ecosystem, offering a wide range of services, including mobile payments, e-commerce, banking, and financial products. Paytm’s innovative approach has significantly disrupted traditional financial services in India, making digital transactions more accessible to millions of users across the country.
The company’s platform allows users to perform a variety of tasks, such as transferring money, paying bills, booking tickets, shopping online, and even investing in mutual funds, all within a single application. This broad range of services has made Paytm a household name in India and has positioned it as a critical player in the country’s journey towards a cashless economy.
Significance of Studying Paytm's Revenue Model:
- Paytm has fundamentally altered the way financial services are delivered in India. By studying its revenue model, one can gain insights into how digital platforms can disrupt traditional industries and create new market opportunities.
- Paytm’s revenue model is multifaceted, encompassing various streams such as transaction fees, merchant services, advertisements, and financial products. Analyzing these revenue streams provides a comprehensive understanding of how digital platforms can monetize their services while scaling their user base.
- Paytm’s growth and success have played a significant role in reshaping India’s digital financial landscape. The company’s strategies have set benchmarks for other fintech companies and have influenced the regulatory environment. By studying Paytm’s approach, one can explore the broader implications for the financial technology sector in
- Paytm’s success story serves as a valuable case study for other emerging markets looking to develop their digital financial infrastructure. The company’s ability to navigate challenges such as regulatory changes, competition, and user adoption offers valuable lessons for other regions.
EMERGENCE OF DIGITAL PAYMENTS:
The evolution of digital payments in India has been a transformative journey, marked by rapid technological advancements and significant policy interventions. In a country where cash was traditionally the dominant mode of transaction, the need for convenient and secure digital payment solutions became increasingly apparent as the economy expanded and urbanized. The proliferation of smartphones and the rise of internet penetration across India laid the groundwork for the digital payment revolution. Government initiatives like the Digital India campaign and the introduction of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) further accelerated this shift, making digital payments more accessible to the masses.
The need for digital payments was driven by several factors. Firstly, the convenience of being able to make transactions anytime and anywhere appealed to a growing population of tech-savvy consumers. Secondly, the security offered by digital payments, with features like two-factor authentication and encryption, provided a safer alternative to carrying cash. Finally, the government’s push towards a cashless economy, particularly after the demonetization in 2016, highlighted the importance of digital payments in curbing black money and improving transparency in financial transactions.
Challenges Faced by Consumers and Businesses:
- In the early stages of digital payment adoption, a significant portion of the population, particularly in rural areas, lacked awareness and digital literacy. This created a barrier to the widespread adoption of digital payment methods.
- Many consumers were initially hesitant to use digital payment methods due to concerns about the security of their financial information. The fear of cyber fraud and data breaches made people cautious about adopting new
- Inadequate digital infrastructure, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas, posed challenges for seamless digital transactions. Issues like inconsistent internet connectivity and limited access to digital devices hindered the adoption of digital
- Small businesses and vendors, accustomed to cash transactions, were initially resistant to adopting digital payment methods. The lack of incentives and the perceived complexity of digital payment systems made it difficult for businesses to transition to cashless
- The cost associated with digital transactions, including merchant discount rates (MDR) and transaction fees, deterred both consumers and businesses from fully embracing digital payment methods.
PAYTM'S FOUNDATION AND DIGITAL WALLET:
Paytm, founded in 2010 by Vijay Shekhar Sharma, began its journey as a mobile recharge platform before quickly expanding into a full-fledged digital wallet service. The idea behind Paytm’s digital wallet was to offer a simple, user-friendly solution that allowed users to load money into their accounts and make transactions directly through their smartphones. This innovation came at a time when India was beginning to embrace mobile technology, but the concept of digital wallets was still relatively new. Paytm capitalized on this opportunity by providing a seamless platform where users could perform various financial transactions, such as paying bills, transferring money, and making purchases both online and offline.
The introduction of the Paytm wallet addressed several pain points associated with traditional payment methods, particularly in a country where cash was still king. One of the primary issues with traditional payment methods was the inconvenience of carrying and managing cash, especially for small transactions. Paytm’s digital wallet eliminated this hassle by allowing users to store money digitally and make payments with just a few taps on their smartphones.
Addressing Traditional Payment Method Pain Points:
- Traditional payment methods often required users to carry cash or visit physical locations to complete transactions. Paytm’s digital wallet provided a more convenient alternative by enabling users to make payments anytime and anywhere, directly from their smartphones. This was particularly beneficial for users in urban areas, where the demand for quick and easy payment solutions was high.
- Cash transactions were often associated with security risks, such as theft or loss, and lacked transparency. Paytm addressed these concerns by offering a secure digital platform with features like encryption and two-factor authentication, ensuring that users’ financial information was protected. Additionally, every transaction made through the Paytm wallet was recorded, providing users with a clear and transparent history of their spending.
- Traditional banking services were not easily accessible to a large portion of India’s population, especially in rural areas. Paytm’s digital wallet helped bridge this gap by providing a financial service that was easy to use and accessible to anyone with a smartphone, regardless of their location or banking status. This democratization of financial services played a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion across the
- Traditional payment methods, such as bank transfers and checks, were often time- consuming and involved lengthy processes. Paytm’s digital wallet streamlined these processes, allowing users to complete transactions instantly. This efficiency was particularly appealing to younger, tech-savvy consumers who valued speed and
- Paytm’s digital wallet was integrated with a wide range of services, from mobile recharges and utility bill payments to shopping and ticket booking. This all-in-one solution made it easier for users to manage their daily financial activities through a single platform, further enhancing its appeal.
DIVERSIFICATION OF SERVICES:
After establishing itself as a leader in digital wallets, Paytm strategically expanded its offerings to include a comprehensive suite of financial services, thereby transforming into a multifaceted financial technology platform. Recognizing the potential to serve a broader range of user needs, Paytm introduced services such as bill payments, mobile recharges, utility payments, and online shopping, all accessible through its app. This diversification allowed Paytm to evolve from a simple digital wallet into a one-stop solution for various financial transactions, significantly enhancing its value proposition to users.
Paytm’s decision to expand into these additional services was driven by the desire to capture a larger share of the rapidly growing digital economy in India. By offering a wide range of services under one platform, Paytm aimed to increase user engagement and retention, ensuring that customers could rely on the app for a variety of daily transactions. This approach not only made the platform more convenient for users but also encouraged them to spend more time within the Paytm ecosystem, leading to higher transaction volumes and increased revenue.
Impact of Diversification on Paytm's Growth and Revenue Generation:
- By diversifying its services, Paytm created multiple touchpoints for user interaction. Whether a user needed to pay a utility bill, recharge their mobile, or book a movie ticket, Paytm provided a seamless platform to complete these tasks. This increased engagement led to higher user retention and a growing user base, which in turn drove the platform’s growth.
- The expansion into various services allowed Paytm to cross-sell products to its existing users. For instance, a user who initially joined Paytm to make digital payments could be introduced to other services like insurance, mutual fund investments, or e-commerce. This cross-selling strategy not only enhanced customer value but also opened up new revenue streams for
- Each additional service introduced by Paytm came with its own set of transaction fees or service charges. For example, Paytm earned revenue from processing fees on utility bill payments, commission on mobile recharges, and merchant discount rates from businesses accepting payments through Paytm. These diverse revenue streams collectively contributed to the company’s overall financial health.
- As Paytm expanded its services, it also built a robust network of partnerships with merchants, service providers, and financial institutions. These partnerships not only expanded the range of services available to users but also generated revenue through merchant commissions and service integration fees.
- Diversification helped Paytm solidify its position as a market leader in the fintech By offering a comprehensive suite of services, Paytm differentiated itself from competitors who were primarily focused on singular services like digital payments or e-commerce. This broad-based approach allowed Paytm to attract a diverse customer base and maintain its competitive edge in the rapidly evolving digital economy.
SCAN AND PAY: QR CODE TECHNOLOGY
Paytm’s introduction of the “Scan and Pay” feature marked a significant innovation in India’s digital payment landscape. Leveraging QR code technology, Paytm enabled users to make quick and secure payments at offline retail outlets by simply scanning a merchant’s QR code using their smartphones. This feature was a game-changer, especially in a market where many small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) operated without the infrastructure for accepting digital payments. The “Scan and Pay” feature allowed these merchants to accept payments without the need for expensive point-of-sale (POS) systems, making it accessible to even the smallest vendors, from roadside stalls to large retail chains.
The simplicity and convenience of “Scan and Pay” resonated with consumers, who found the process of scanning a QR code and completing a transaction in seconds far easier than dealing with cash or cards. The technology required no complex setup or additional hardware, only a smartphone, making it highly appealing in a country where smartphone penetration was rapidly increasing.
Adoption by Consumers and Merchants:
- The “Scan and Pay” feature was quickly adopted by consumers due to its ease of use, speed, and security. Users appreciated the ability to make payments without carrying cash or cards, which aligned with the broader push towards a cashless economy. Additionally, Paytm’s frequent cashback offers and discounts for QR code payments incentivized users to choose this method over traditional payment forms. This convenience, combined with financial incentives, drove rapid adoption among a diverse user base, from urban professionals to rural consumers.
- For merchants, particularly small businesses and informal vendors, “Scan and Pay” provided an affordable and straightforward way to accept digital payments. The zero- cost setup and minimal technical requirements made it an attractive option for businesses that had previously been cash-only. Paytm provided free QR code stickers, which merchants could display at their outlets, further lowering the barrier to entry. As a result, the adoption of QR code payments spread rapidly across various sectors, including retail, food services, and transportation.
- The adoption of QR code technology by both consumers and merchants significantly expanded Paytm’s footprint in the offline retail space. It allowed the company to tap into previously underserved markets, including rural areas and small towns, where traditional digital payment methods had limited reach. The widespread use of “Scan and Pay” also enhanced Paytm’s data analytics capabilities, enabling the company to offer personalized services and targeted promotions to users based on their transaction
- The introduction of “Scan and Pay” strengthened the relationship between merchants and customers by providing a seamless payment experience. Merchants were able to process payments quickly, reducing checkout times and improving customer Moreover, the integration of digital payments into everyday transactions helped foster trust between merchants and customers, as digital records of transactions added a layer of transparency and security.
PAYTM FOR BUSINESS:
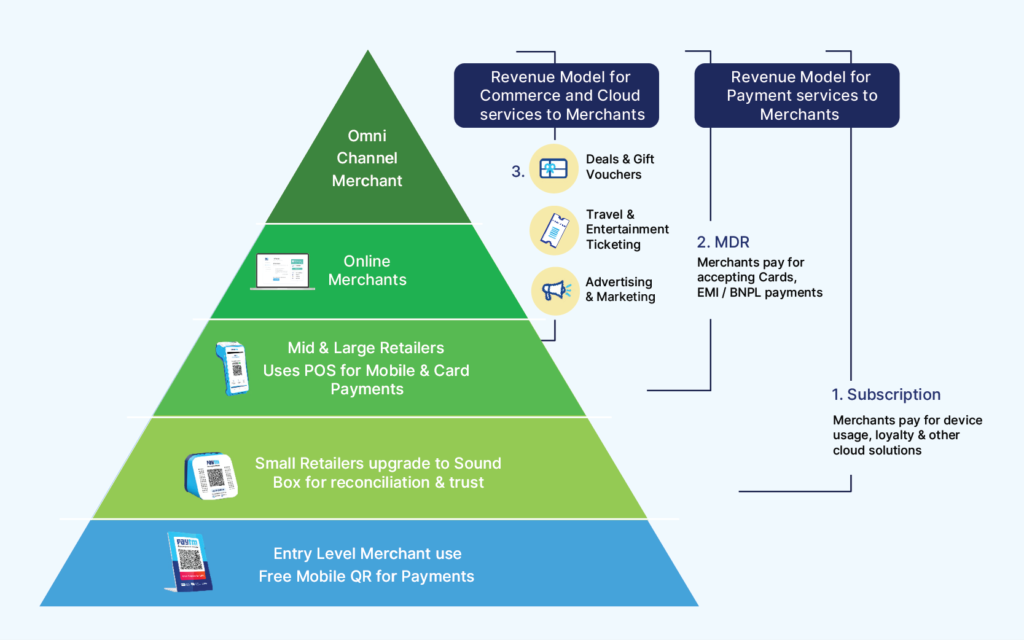
Paytm’s expansion into providing solutions for businesses represents a strategic move to broaden its market beyond individual consumers to include merchants and small businesses. The company introduced a range of services tailored to meet the diverse needs of business owners, such as payment gateways, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and tools for online store creation. The Paytm payment gateway offers a seamless and secure method for businesses to accept digital payments across various channels, including websites, apps, and in-store transactions. This service is particularly beneficial for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that lack the resources to develop complex payment infrastructures on their own.
The POS systems provided by Paytm are designed to integrate easily with existing business operations, allowing merchants to manage sales, inventory, and customer data in a streamlined manner. These systems are also equipped to accept multiple forms of payment, including credit and debit cards, UPI, and Paytm Wallet, thus catering to the varied preferences of customers. Additionally, Paytm’s online store creation tools empower small businesses to establish an e-commerce presence without the need for significant technical expertise. This suite of business solutions not only simplifies operations for merchants but also expands their reach to a broader customer base, contributing to their growth and profitability.
DIGITAL BANKING SERVICES:
Paytm’s entry into the digital banking space with the launch of Paytm Payments Bank marked a significant expansion of its financial services. Paytm Payments Bank offers savings accounts, fixed deposits, and other banking services, bridging the gap between digital wallets and traditional banking. This move allowed Paytm to capture a segment of the market that was underserved by traditional banks, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas where access to banking services is limited. By offering interest-bearing savings accounts with no minimum balance requirements, Paytm Payments Bank attracted a large number of users who were previously unbanked or underbanked.
The integration of banking services into the Paytm ecosystem not only enhanced user convenience but also provided Paytm with new revenue streams through banking fees, interest income from fixed deposits, and transaction charges. Additionally, the data generated from these banking services enabled Paytm to offer personalized financial products, such as loans and insurance, further strengthening its position in the financial services market.
WEALTH MANAGEMENT AND INVESTMENT:
Expanding into wealth management and investment services through the Paytm Money platform, Paytm sought to cater to the growing demand for accessible investment options among its user base. Paytm Money offers a wide range of financial products, including mutual funds, stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and more. The platform is designed to be user-friendly, making it easier for individuals, especially first-time investors, to navigate the complexities of investing.
By offering these services, Paytm not only diversified its product offerings but also attracted a new segment of users—those interested in growing their wealth through investments. This move also opened up additional revenue streams for Paytm, including commissions on mutual fund sales, brokerage fees on stock trades, and subscription fees for premium services. The expansion into wealth management positioned Paytm as a comprehensive financial platform, catering to both everyday financial needs and long-term investment goals.
ENTERTAINMENT AND LIFESTYLE:
Paytm’s partnerships in the entertainment and lifestyle sectors have further enriched its ecosystem, enabling users to book tickets for movies, events, flights, and hotels directly through the Paytm app. These partnerships with leading brands and service providers have made Paytm a go-to platform for a wide range of lifestyle needs. For instance, Paytm’s integration with major movie theater chains and event organizers allows users to book tickets seamlessly, often with the added benefit of cashback offers and discounts.
In the travel sector, Paytm’s collaboration with airlines, bus services, and hotel chains offers users a comprehensive booking experience, from flights to accommodations, all within the app. These partnerships not only enhance user convenience but also drive significant
traffic to the platform, contributing to Paytm’s overall revenue. The ability to bundle services, such as booking a movie ticket and paying for a meal at the theater using Paytm, creates a holistic user experience that encourages repeat use and deepens user engagement within the Paytm ecosystem.
ADVERTISING AND PROMOTIONS:
Paytm has effectively monetized its large user base by offering advertising and promotional opportunities to brands looking to reach a targeted audience. Through its platform, Paytm enables brands to run targeted campaigns, leveraging user data to deliver
personalized offers and advertisements. This personalized approach ensures that users receive relevant promotions, increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
For businesses, advertising on Paytm provides access to millions of active users, allowing them to reach potential customers efficiently. Paytm generates revenue from these advertisements, as well as from commissions on promotions and sales driven through its platform. The success of these targeted campaigns not only benefits advertisers but also enhances the overall user experience by providing them with offers that align with their interests and spending habits.
FINANCIAL SERVICES MARKETPLACE:
As a financial services aggregator, Paytm has established itself as a one-stop marketplace where users can access a variety of financial products, including insurance, loans, and credit cards. By partnering with leading financial institutions, Paytm offers a wide selection of products tailored to meet the diverse needs of its users. For example, users can compare and purchase health insurance, apply for personal loans, or get a credit card directly through the Paytm app, simplifying the process and saving time.
Paytm benefits from these partnerships through commissions earned on each product sold or service facilitated through its platform. Additionally, the aggregation of financial services strengthens Paytm’s value proposition, attracting users who prefer the convenience of managing all their financial needs in one place. This comprehensive approach not only enhances customer loyalty but also drives additional revenue streams for Paytm, solidifying its position as a key player in the Indian financial services market.
MONETIZATION OF USER DATA:
The monetization of user data has become a significant revenue stream for many digital platforms, including Paytm. By analyzing the vast amounts of data generated by its users, Paytm can offer targeted advertising, personalized offers, and financial products that align with individual user profiles. This data-driven approach enables Paytm to optimize its marketing strategies, enhance user engagement, and maximize its revenue potential.
However, the collection and use of personal data raise important ethical considerations, particularly concerning user privacy and data security.
Balancing User Privacy and Revenue Generation:
- Transparency and Trust:
To balance user privacy with revenue generation, Paytm must prioritize transparency in its data practices. This involves clearly communicating to users how their data will be used, who it will be shared with, and the benefits they receive in return. Building trust through transparency is crucial, as it can help mitigate concerns and ensure that users feel comfortable with the platform’s data practices.
- Data Minimization and Security:
Paytm can also adopt data minimization principles, collecting only the data necessary for specific purposes and ensuring robust security measures are in place to protect this data. By limiting data collection and focusing on safeguarding user information, Paytm can reduce the risk of data breaches and enhance its ethical standing.
- User Control and Opt-Out Options:
Empowering users with control over their data is another essential aspect of balancing privacy with monetization. Paytm should offer clear and accessible options for users to opt out of data sharing or to customize their privacy settings according to their comfort level. This approach not only respects user autonomy but can also improve user satisfaction and loyalty.
- Ethical Monetization Strategies:
Finally, Paytm can explore ethical monetization strategies that do not rely heavily on user data. For example, Paytm could focus on expanding subscription- based services, where users pay for enhanced features rather than having their data monetized. This model could provide a sustainable revenue stream while respecting user privacy.
INTERNATIONAL EXPANSION:
Paytm’s international expansion has been a strategic move to leverage its success in the Indian market and capture growth opportunities in other regions. By extending its mobile wallet and payment solutions to select countries, Paytm aims to replicate its domestic success on a global scale and tap into new revenue streams. This expansion strategy involves offering Paytm’s core services, including mobile payments, bill payments, and e-commerce solutions, in markets that show potential for digital financial services.
Efforts and Initiatives:
- Paytm’s initial international expansion efforts involved partnerships and joint ventures to enter new markets. For instance, Paytm has established a presence in markets like Canada and Southeast Asia, where it has collaborated with local businesses to integrate its payment solutions. These partnerships help Paytm navigate regulatory landscapes and adapt its services to meet local needs.
- To cater to diverse international markets, Paytm has tailored its offerings to align with regional preferences and regulatory requirements. This includes adapting payment solutions to local currencies, integrating with existing payment infrastructures, and ensuring compliance with local financial regulations. By localizing its services, Paytm aims to enhance user acceptance and drive adoption in new
- Paytm has leveraged its technological expertise to offer innovative payment solutions This includes features like QR code payments, digital wallets, and payment gateways, which have been successfully implemented in various countries. Paytm’s focus on technology and user experience helps differentiate its services from local competitors and attract international customers.
Opportunities of Global Expansion:
- Many regions, especially in Southeast Asia and Africa, are experiencing rapid growth in digital payment adoption. These markets present significant opportunities for Paytm to introduce its services and capture a share of the expanding digital economy. As more consumers and businesses move towards digital transactions, Paytm stands to benefit from this trend.
- Expanding internationally allows Paytm to diversify its revenue streams and reduce reliance on the Indian market. By tapping into new markets, Paytm can generate additional income through transaction fees, partnerships, and localized services. This diversification also helps mitigate risks associated with economic fluctuations in a single
- Forming strategic partnerships and alliances with local players can facilitate smoother market entry and expansion. These collaborations provide valuable insights into local market dynamics, help build credibility, and enable Paytm to leverage existing networks and infrastructure.
- Successfully expanding into international markets enhances Paytm’s global brand recognition and reputation. A strong international presence can bolster Paytm’s position as a leading fintech player and open up further opportunities for growth and
COVID-19 IMPACT AND DIGITAL ADOPTION:
The COVID-19 pandemic profoundly accelerated the adoption of digital payments and financial services, a trend that significantly benefited Paytm. As global lockdowns and social distancing measures were implemented, consumers and businesses rapidly shifted towards digital and contactless payment methods to minimize physical contact and reduce the risk of virus transmission. This shift was particularly evident in India, where Paytm capitalized on the growing demand for digital solutions.
- The pandemic led to a surge in digital payment transactions as people sought safer alternatives to cash. Paytm, with its established digital wallet and payment solutions, saw a substantial increase in user engagement and transaction volumes. The convenience and safety of digital payments became a crucial factor in consumer behavior, driving more individuals to adopt Paytm’s services for everyday transactions, bill payments, and online
- Paytm also experienced growth in its financial services offerings during the With more people looking for online banking, investment, and insurance options, Paytm’s expanded suite of services, including Paytm Payments Bank and Paytm Money, gained traction. The increased demand for remote financial services provided a significant boost to Paytm’s user base and revenue.
- The pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital payment solutions among merchants, particularly small and medium-sized businesses that had previously relied on cash transactions. Paytm’s QR code payments and POS systems became essential tools for businesses to accept contactless payments, helping them to continue operations during lockdowns and attract customers who preferred digital
- Government initiatives and policies aimed at promoting digital payments also played a role in accelerating adoption. Efforts to digitize government transactions and provide incentives for digital payments further supported Paytm’s growth during the These policies not only increased digital payment adoption but also reinforced Paytm’s position as a leading digital financial platform in India.
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly accelerated the adoption of digital payments, benefiting Paytm by expanding its user base and revenue. Looking ahead, Paytm’s focus on integrating blockchain and AI into its services represents a commitment to innovation. However, the company must navigate challenges such as intense competition, regulatory compliance, and maintaining user trust to sustain its growth and market leadership.
CONCLUSION:
The case study of Paytm reveals a compelling narrative of how a digital payment platform evolved into a comprehensive financial ecosystem, transforming the mobile payments landscape in India. Paytm’s journey from a digital wallet service to a multifaceted financial services provider underscores its strategic approach to revenue generation and market expansion.
Key Findings:
- Paytm initially emerged as a digital wallet, offering users a convenient way to load money and make transactions through smartphones. This foundational service addressed key pain points associated with traditional payment methods, such as the need for cash handling and the inefficiencies of paper-based
- The company expanded its offerings to include bill payments, mobile recharges, utility payments, and more, establishing itself as a versatile platform. This diversification not only contributed to Paytm’s revenue growth but also created a comprehensive ecosystem that catered to a wide range of financial
- Paytm introduced features like the “Scan and Pay” QR code technology, which facilitated contactless payments at offline retail This innovation enhanced the convenience of transactions for both consumers and merchants, further entrenching Paytm’s position in the market.
- Paytm’s foray into providing business solutions, such as payment gateways and POS systems, alongside the launch of Paytm Payments Bank, highlighted its strategic expansion into banking and business services. These moves not only broadened Paytm’s service portfolio but also created new revenue
- The introduction of Paytm Money for wealth management and investment services, along with partnerships in the entertainment and lifestyle sectors, showcased Paytm’s ability to tap into diverse revenue sources and enhance its user engagement.
- Paytm’s use of user data for targeted advertising and personalized offers underscored the importance of data-driven strategies in revenue generation. However, this approach also raised ethical considerations regarding user privacy and data security.
- Paytm’s efforts to expand internationally, leveraging partnerships and localized offerings, demonstrated its ambition to capture global market opportunities. The challenges of regulatory compliance, competition, and cultural differences were notable, yet the opportunities for growth in emerging markets were
- The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated digital payment adoption, benefiting Paytm by expanding its user base and increasing transaction volumes. This period highlighted the role of digital solutions in providing safe and convenient financial services during times of crisis.
- Paytm’s ongoing investment in technologies like blockchain and AI reflects its commitment to innovation. However, the company faces challenges related to competition, regulatory compliance, and maintaining user trust, which are critical for sustaining growth and market leadership.
Lessons for Other Fintech Companies:
- Diversifying service offerings can create a comprehensive financial ecosystem that attracts a broader user base and generates multiple revenue streams. Companies should explore opportunities to expand their services beyond core offerings to meet diverse customer needs.
- Investing in emerging technologies such as AI and blockchain can enhance service delivery, improve security, and drive innovation. Staying ahead of technological trends is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
- Providing a seamless and user-friendly experience is key to driving adoption and user Features that enhance convenience, such as contactless payments and personalized recommendations, can significantly impact user satisfaction and loyalty.
- Understanding and complying with regulatory requirements in different markets is essential for successful expansion and operation. Companies must stay informed about regulatory changes and adapt their practices
- Building and maintaining user trust is vital, especially when dealing with personal data and financial transactions. Transparency in data practices and robust security measures are necessary to foster trust and ensure long-term user
Paytm’s success demonstrates the effectiveness of a well-rounded strategy that combines innovation, diversification, and user-centric solutions. Other fintech companies can draw valuable lessons from Paytm’s approach to building a comprehensive financial ecosystem and addressing the challenges of a rapidly evolving market.



